|
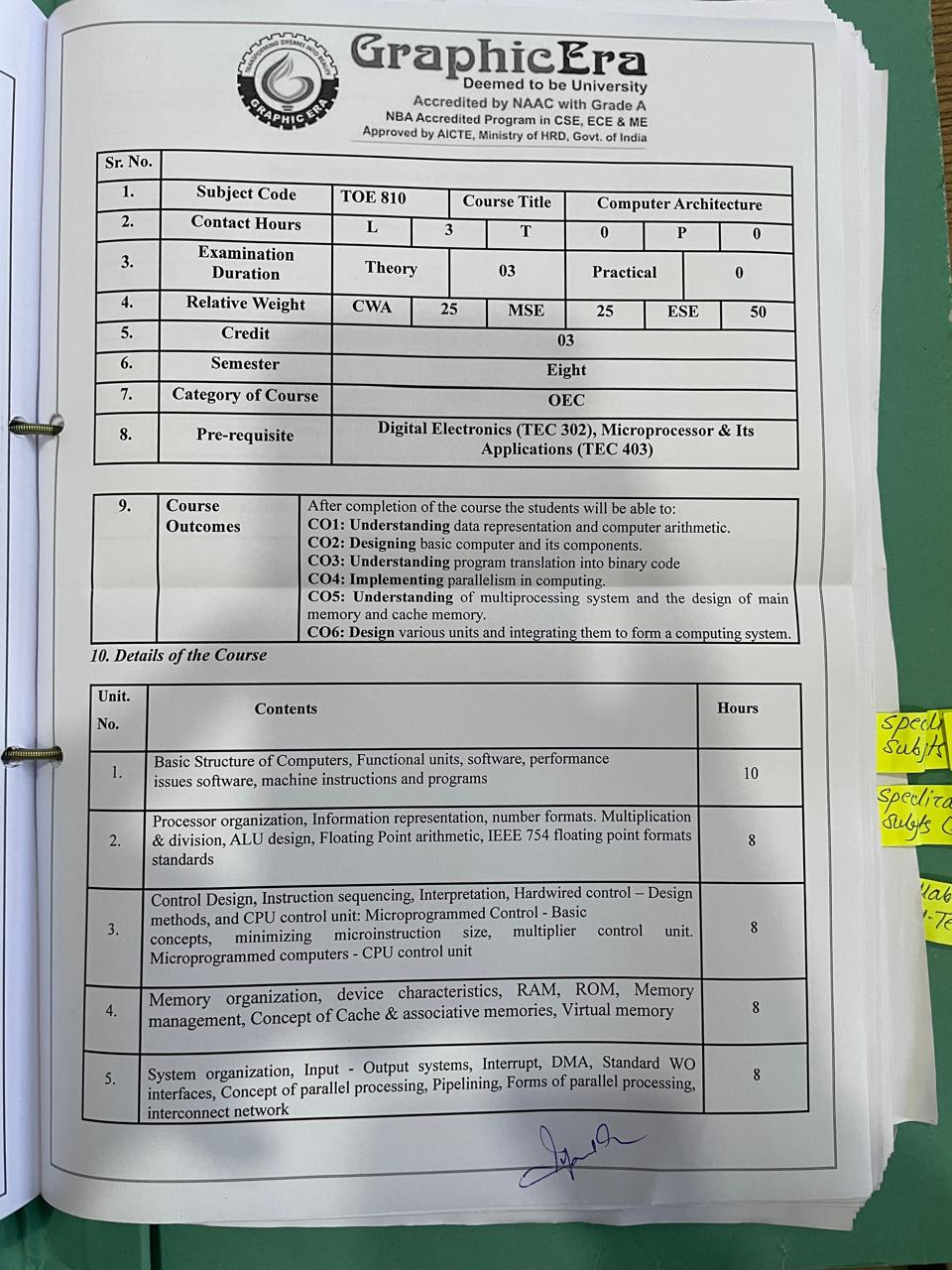
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering |
|||||||
|
B. Tech in Electronics and Communication Engineering |
|||||||
|
Semester |
Eighth |
Subject Title |
Mobile Ad hoc Networks |
Code |
TEC 857 |
||
|
Course Component |
Credits |
Contact Hours |
L |
T |
P |
||
|
Program Elective Course (PEC) (VI) |
03 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|||
|
Examination Duration (Hrs) |
Theory |
Weightage: Evaluation |
CWA |
MSE |
ESE |
||
|
03 |
25 |
25 |
50 |
||||
|
Pre-requisite: Wireless Communication |
|||||||
|
Course Outcomes |
|||||||
|
Upon completion of this course, the students will be able to |
|||||||
|
CO 1 |
Understand the concept of ad hoc wireless networking, IEEE 802.11, IEEE 802.16 (Wi-Max), Bluetooth, IrDA, RF home, design and operation of ad hoc network, their design issues and available solution. |
||||||
|
CO 2 |
Understand MAC layer protocols and design issues of MAC protocols. |
||||||
|
CO 3 |
Understand and remember proactive, reactive and hybrid routing protocols and routing mechanism. |
||||||
|
CO 4 |
Understand energy management in ad hoc network. |
||||||
|
CO 5 |
Understand Security attacks and QoS provisioning in ad hoc network. |
||||||
|
CO 6 |
Develop and design efficient wireless mobile ad hoc networks. |
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Unit No. |
Content |
Hours |
|||||
|
Unit 1: |
Introduction: Ad hoc networking: An introduction. Model of operation, Symmetric links, Fundamental of wireless networks, Bluetooth, IrDA, Comparison of bluetooth and IrDA, Home RF, 802.11, 802.16(Wi-Max), Hotspot, Difference between cellular and ad hoc networks, Technical and research challenges. DoD perspective. |
8 |
|||||
|
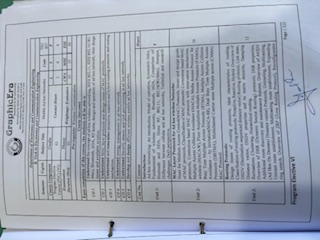
Unit 2: |
MAC Layer Protocols for Ad hoc wireless Networks: Need for Medium Access Control(MAC) Protocols, Issues and design goals of MAC protocols, Classification of MAC protocols: Contention based MAC protocols, Contention based MAC protocols with reservation mechanism, Multiple Access Collision Avoidance (MACA), Media Access Protocol for wireless (MACAW), Floor Acquisition Multiple Access Protocols (FAMA), Busy Tone Multiple Access Protocols (BTMA), Multiple Access Collision Avoidance – by Invitation(MACA-BI), Dual Busy Tone Multiple Access Protocols (DBTMA), Multichannel Carrier sense Multiple access (CSMA) MAC Protocol. |
10 |
|||||
|
Routing Protocols: Design issues of routing protocols, Ideal characteristics of routing, Classification of routing protocols: Proactive, Reactive, Hybrid. Overview of DSDV (Destination sequenced distance vector) Routing protocol, Link state, Distance vector, DSDV properties and its merits demerits, Damping fluctuations. Clustering, Hierarchical routing. Overview of DSR (Dynamic Source Routing) protocols: DSR properties, Additional route discovery and maintenance features. Overview of AODV (Ad Hoc On Demand Distance vector) Protocols, Unicasting, Multicasting, Unicast route establishment, Multicasting route establishment, Expanding ring search. Overview of ZRP (Zone Routing Protocol), Reconfigurable wireless networks, Intrazone, Interzone routing protocols. Overview of OLSR (Optimized Link State Routing) Protocol, Multipoint relays (MPRs), Protocol functioning, Core functioning. |
12 |
||||||
|
Energy management Energy management system in Ad Hoc networks, Power issues, Smart batteries, and Associatively based routing, Effects of beaconing of battery life, Maximum lifetime routing. |
5 |
||||||
|
Network Security Attacks and Quality of Service Security in Ad Hoc wireless networks, Network security requirements, Issues and challenges in security provisioning, Network security attacks. QoS in Ad Hoc wireless networks, Issues and challenges, Classification of QoS solutions. Wireless sensor networks, Issues and challenges, Sensor network architecture, Flooding gossiping, Rumor routing, Quality of sensor networks, Evolving standards. |
7 |
||||||
|
Total Hours |
42 |
||||||
|
Textbooks |
|
|
1. |
C. Perkins, “Ad Hoc Networking”, Addison-Wesley Professional,1st Edition, 2008. |
|
2. |
C. Siva Ram Murthy, and B. S.Manoj, “Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Architecture and Protocols”, Pearson Education 2nd Edition, 2004. |
|
Reference Books |
|
|
3. |
S. Basagni, And M. Conti, “Mobile Ad Hoc Networking: Cutting Edge Directions”, John Wiley & Sons, 2nd Edition, 2013. |
|
Mode of Evaluation |
Test / Quiz / Assignment / Mid Term Exam / End Term Exam. |
- Teacher: ANZAR AHMAD
|
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering |
|||||||
|
B. Tech in Electronics and Communication Engineering |
|||||||
|
Semester |
Eighth |
Subject Title |
Neural Networks & Machine Learning |
Code |
TEC 856 |
||
|
Course Component |
Credits |
Contact Hours |
L |
T |
P |
||
|
Program Elective Course (PEC) (VI) |
03 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|||
|
Examination Duration (Hrs) |
Theory |
Weightage: Evaluation |
CWA |
MSE |
ESE |
||
|
03 |
25 |
25 |
50 |
||||
|
Pre-requisite: Basic Probability Theory and Basic Linear Algebra |
|||||||
|
Course Outcomes |
|||||||
|
Upon completion of this course, the students will be able to |
|||||||
|
CO 1 |
Understand the basics of neural network and its parameters. |
||||||
|
CO 2 |
Examine the feed forward network and its implementation. |
||||||
|
CO 3 |
Analyse the concepts of pattern analysis and implementation of support vector machine. |
||||||
|
CO 4 |
Investigate self-organizing map and pattern clustering. |
||||||
|
CO 5 |
Evaluate different feedback network, such as Hopfield, Boltzmann machine. |
||||||
|
CO 6 |
Develop neural network for specific applications. |
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
Unit No. |
Content |
Hours |
|||||
|
Unit 1: |
Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks: Biological neural networks, ANN application overview, Pattern analysis tasks: Classification, Regression and clustering, Computational models of neurons, Structures of neural networks, Learning principles, Supervised, Unsupervised and reinforcement learning. Linear Models of Learning and Classification: Polynomial curve fitting, Bayesian curve fitting, Linear basis function models, Bias-variance decomposition, Bayesian linear regression, Least squares for classification, Logistic regression for classification, Bayesian logistic regression for classification. |
12 |
|||||
|
Unit 2: |
Feed Forward Neural Networks: Pattern classification using perceptron, Multilayer feed forward neural networks (MLFNNs), Pattern classification using MLFNNs, error and back propagation learning, Fast learning methods: Conjugate gradient method, Auto-associative neural networks, Bayesian neural networks. |
8 |
|||||
|
Unit 3: |
Radial Basis Function Networks: Regularization theory, RBF networks for function approximation, RBF networks for pattern classification. Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis: Statistical learning theory, Support vector machines for pattern classification, Support vector regression for function approximation, Relevance vector machines for classification and regression. |
8 |
|||||
|
Unit 4: |
Self-Organizing Maps: Pattern clustering, Topological mapping, Kohonen’s self organizing map, Competitive learning, Learning vector quantizers, Counter propagation networks, Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART). |
6 |
|||||
|
Unit 5: |
Feedback Neural Networks: Pattern storage and retrieval, Hopfield model, Boltzmann machine, Recurrent neural networks. Applications of Neural Networks and Machine Learning: Case studies. |
6 |
|||||
|
Total Hours |
42 |
||||||
- Teacher: SANTOSH SHANKARRAO Saraf
|
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering |
|||||||
|
B. Tech in Electronics and Communication Engineering |
|||||||
|
Semester |
Eighth |
Subject Title |
Satellite Communications |
Code |
TEC 851 |
||
|
Course Component |
Credits |
Contact Hours |
L |
T |
P |
||
|
Program Elective Course (PEC) (V) |
03 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|||
|
Examination Duration (Hrs) |
Theory |
Weightage: Evaluation |
CWA |
MSE |
ESE |
||
|
03 |
25 |
25 |
50 |
||||
|
Pre-requisite: Wireless Communication and Microwave Engineering |
|||||||
|
Course Outcomes |
|||||||
|
Upon completion of this course, the students will be able to |
|||||||
|
CO 1 |
Understand basic concepts of orbital mechanism and launch vehicle. |
||||||
|
CO 2 |
Apply the technologies for satellite & earth station architecture, and applications. |
||||||
|
CO 3 |
Analyse the satellite link for the optimum link performance. |
||||||
|
CO 4 |
Evaluate the modulation and coding schemes for a given satellite communication link. |
||||||
|
CO 5 |
Understand various satellite systems - worldwide and Indian scenario. |
||||||
|
CO 6 |
Design prototype satellite communication link for given specifications. |
||||||
- Teacher: Anurag Vidyarthi